测试环境
- 两台RedHat6.5 64位虚拟机
- JDK版本:1.7.0_21
- 测试文件大小:212MB
NIO发送测试
1.服务端代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
if(args.length != 1){
System.out.println("Usage : java -jar ServerTcpListener.jar port");
return;
}
try {
final ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(Integer.parseInt(args[0])));
Thread th = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
while(true){
SocketChannel socketChannel =
serverSocketChannel.accept();
if(socketChannel != null){
receiveFile(socketChannel);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
th.run();
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void receiveFile(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws IOException {
final Path filePath = Paths.get("test"); //要将接收的文件写到当前目录的test文件中
FileChannel fileChannel = (FileChannel.open(filePath,
EnumSet.of(StandardOpenOption.CREATE_NEW,
StandardOpenOption.WRITE,
StandardOpenOption.TRUNCATE_EXISTING)));
//先获取文件大小,这里我约定前8个字节表示文件大小
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(8);
socketChannel.read(buf);
buf.flip();
long fileSize = buf.getLong();
System.out.println("fileSize :" + fileSize);
//接收文件内容
fileChannel.transferFrom(socketChannel, 0, fileSize);
fileChannel.close();
}
2.客户端代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
if(args.length != 3){
System.out.println("Usage : java -jar ClientTcpSend.jar ipaddress port filename");
return;
}
SocketChannel socketChannel;
try {
socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(args [0], Integer.parseInt(args[1])));
final Path filePath = Paths.get(args[2]);
FileChannel fileChannel = (FileChannel.open(filePath,
EnumSet.of(StandardOpenOption.READ)));
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//用来发送文件大小
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(8);
buf.asLongBuffer().put(fileChannel.size());
socketChannel.write(buf);
//发送文件内容
fileChannel.transferTo(0, fileChannel.size(), socketChannel);
fileChannel.close();
socketChannel.close();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Total use " + (end - start) + "ms");
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3.测试过程
将两个jar包传到不同的服务器中,在服务端启动监听
java -jar NIOServer.jar 12345
在客户端向服务端发送文件,如下:
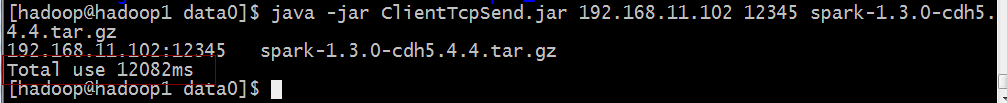
java -jar java -jar NIOClient.jar 192.168.11.102 12345 spark-1.3.0-cdh5.4.4.tar.gz
4.测试结果
服务器端
客户端
Read/Write发送测试
1.测试过程
使用TCP建立socket连接,然后从客户端向服务端发送。代码太简单就不粘贴了。
2.测试结果
客户端
服务端:略
总结
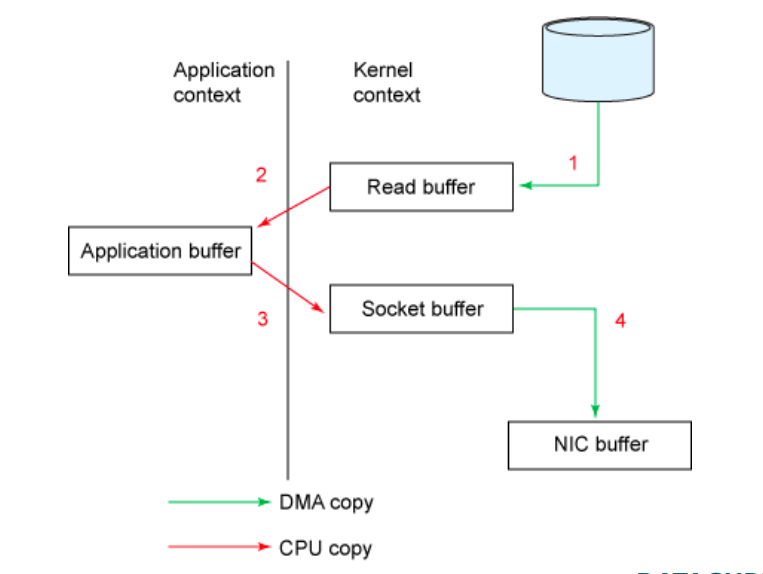
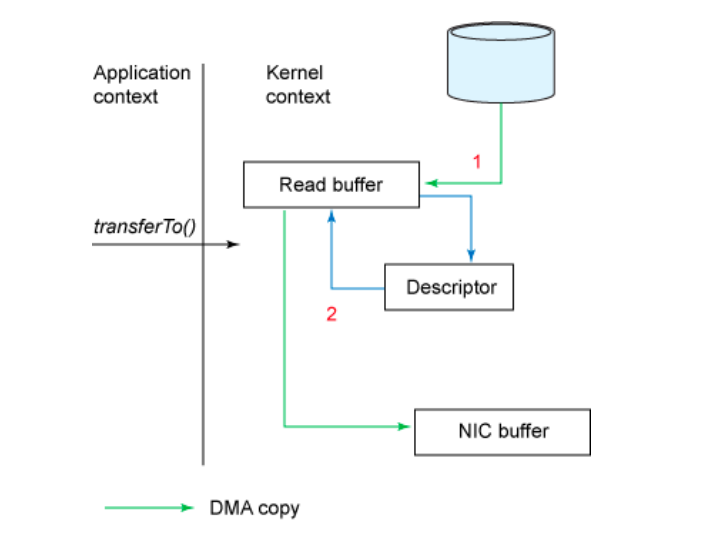
由上述测试可以看到NIO与Read/Write在网络传输文件过程中的差异。NIO消除了CPU的数据拷贝,直接在内核空间中,将数据从文件缓冲区发送到网卡缓冲区中进行发送。而传统模式下数据从文件传输到网络需要4次数据拷贝,4次上下文切换和2次系统调用。如下:
传统模式下发送文件过程
NIO transferTo/transferFrom发送文件过程
Java NIO的transferTo/transferFrom与read/write方式文件网络数据传输测试对比


楼主采用的方法有点问题。在客户端发送文件时,transferTo方法不应该传入fileChannel.size(),默认只能传8192字节即8KB,得采用循环发送的方式才能完整传输文件。
原来:
fileChannel.transferTo(0, fileChannel.size(), socketChannel);
修改后:
long position = 0;
long maxCount = 8192;
while (position < fileChannel.size()) {
position += fileChannel.transferTo(position, maxCount, socketChannel);
}
感谢提示,fileChannel默认缓冲区是8192,使用你提供的这种方式应该是比较稳妥的一种方式,不过我这边测试过程汇总,直接使用fileChannel.size()也发送成功了,接下来我仔细研究一下。